Understanding Children’s Rights
The application, implementation, and interpretation of the 8 Fundamental Rights of the child is guided and determined by the 4 Guiding Principles of the Convention on the Rights of the Child; the principle of non-discrimination, the “best interests of the child” principle, the principle of life, survival and development, and the principle of inclusion and participation.

Right to Life
The right to life is considered the most fundamental human right, encompassing the protection and preservation of life for all.

Right to Education
Every child has the right to a quality education. This principle is enshrined in international agreements and recognized as crucial for individual and societal development.

Right to Food
The right to adequate food is a fundamental human right. Without it, children face significant mental and physical health risks, which in the most extreme cases can be life-threatening.

Right to Water
Water is an essential right for all, and yet, its importance is often overlooked. For many, the right to water remains a theoretical promise rather than a lived reality.
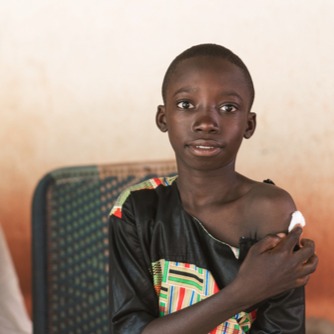
Right to Health
The right to health is a fundamental entitlement for every child, as enshrined in the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child, which states that all children are entitled to the highest attainable standard of health.

Right to Identity
Every child has the right to an identity from birth. This fundamental human right is particularly significant for children, as it affirms their existence in society and acknowledges their uniqueness.

Right to Freedom
The right to freedom is a fundamental right protected under international law and granted to all human beings, including children.

Right to Protection
All children are entitled to fundamental rights ensuring protection from harm, including abuse, exploitation, neglect and other threats to physical and mental well-being.

