Children of Hungary
Realizing Children’s Rights in Hungary


Despite efforts undertaken by Hungary, for example the 2003 equal treatment law, acts of discrimination continue against the Roma, an ethnic minority of Indian origin. In practice, access to health services and education for Roma children is still limited. In addition their parents have more problems finding housing or a job, and Roma families are far more affected by poverty than the rest of the Hungarian population. The Roma population is a victim of racism and intolerance, and the police commit many acts of violence against them.
Population: 9.976 million Life expectancy: 74,6 years |
Main problems faced by children in Hungary:
Poverty
 Even though Hungary is a developed country, the poverty rate is alarming, especially for single-parent families, large families, and families caring for a disabled child. The Roma are the most affected by poverty: 40% of the Roma population is considered poor versus 6.9% of the Hungarian population. The life expectancy for this disadvantaged population is only 60 compared to 74 for the rest of Hungary.
Even though Hungary is a developed country, the poverty rate is alarming, especially for single-parent families, large families, and families caring for a disabled child. The Roma are the most affected by poverty: 40% of the Roma population is considered poor versus 6.9% of the Hungarian population. The life expectancy for this disadvantaged population is only 60 compared to 74 for the rest of Hungary.
Right to Education
Roma children, particularly girls who are often victims of harassment, have a limited access to education or leave school early.
There has been significant progress in primary education access, but still only 1% of young Roma children graduate from higher education.
There is segregation at school between Roma and non-Roma children. Legally minority languages can be taught at school but this is rarely the case in practice. Consequently, 80% of the Roma population has partially lost knowledge of their language. Concerning education as a human right, it is not sufficiently instilled in Hungarian children, particularly in rural and poor communities and among minorities. Finally, corporal punishment is still practiced despite its prohibition.
Right to Health
Roma children have less access to care than other Hungarian children. The infant mortality rate is higher among Roma children than the rest of the Hungarian population.
Main problems include a high rate of child suicide, high incidence of drug addiction among adolescents and the lack of mental health services for children and adolescents.
Child Marriage
 In Hungary, the minimum age for marriage is 16, which is too young according to UN observers who propose increasing the age to 18. In addition, a lack of concern by authorities on this subject allows child marriage to occur among the Roma population.
In Hungary, the minimum age for marriage is 16, which is too young according to UN observers who propose increasing the age to 18. In addition, a lack of concern by authorities on this subject allows child marriage to occur among the Roma population.
Children with Disabilities
Not all schools have been adapted to receive disabled children, meaning these children have limited access to education, despite policies put in place to help children with disabilities. At the same time they are often victims of violence, abuse and exploitation and can be marginalized and rejected by society.
Children of Asylum Seekers, Refugees and Migrants
Many cases of violation of the rights of asylum seekers, refugees and migrants are reported in Hungary. They are constantly subjected to racism and xenophobia. Children are detained with their families in transit camps.
Abuse
Although corporal punishment is prohibited, many Hungarian children suffer beatings and sexual abuse. In the majority of cases these acts are committed within the family. In addition, victims of abuse are not properly cared for by authorities.
Sexual Exploitation
The trafficking of women and girls for sexual exploitation and domestic servitude persists in Hungary. The country should urgently adopt a national plan of action to fight against this phenomenon and increase assistance for victims of trafficking.
 Justice and Juvenile Detention
Justice and Juvenile Detention
Hungarian legislation takes the child’s participation into account for all decisions concerning them. However, in practice, the word of the children of asylum seekers, refugees, and Roma is rarely taken into consideration in judicial and administrative decisions.
A very troubling fact in Hungary; sometimes children are detained with adults. Most detained children are Roma. Some juvenile detainees are victims of abuse and violence from the police, but these children are not listened to and their abusers are rarely convicted.
Juvenile detainees do not have the mandatory right to legal protection like the right to an attorney. In general, the Hungarian juvenile justice system is not in agreement with the Convention on the Rights of the Child.
Exposure to the Dangers of the Internet
Hungarian children are not adequately aware of the dangers one can encounter on the Internet and through other media forms. They can easily access violent, racist, or pornographic videos unsuitable for their age.

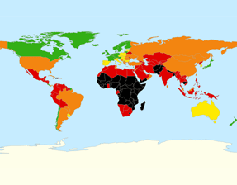
 Realization of Children’s Rights Index
Realization of Children’s Rights Index